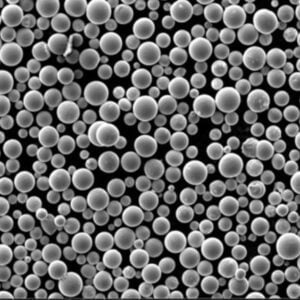
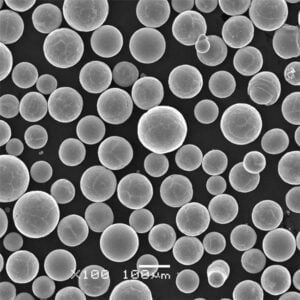
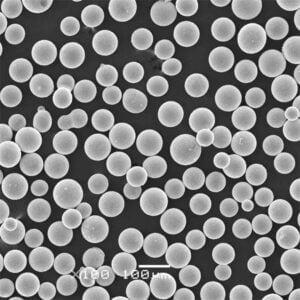
Maraging Çelik C250 Toz
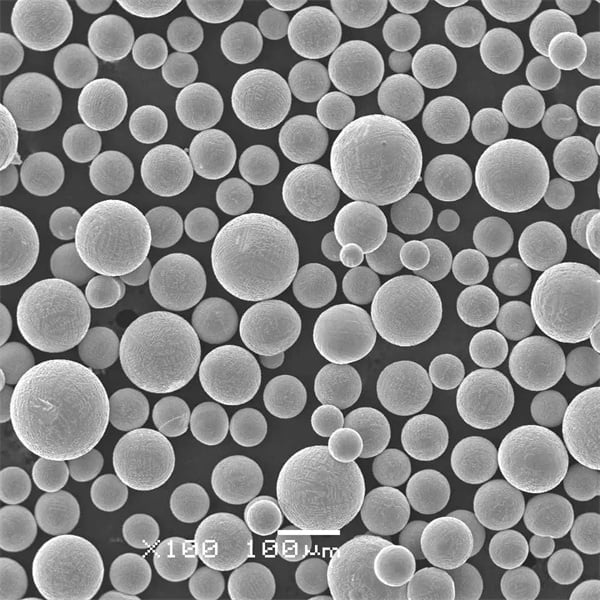
Maraging Steel C250 Powder, dövülebilirliğini kaybetmeden ultra yüksek mukavemeti ve tokluğu ile dikkat çeken 18% nikel, kobalt ile güçlendirilmiş çelik (C250) alaşımıdır. Maraging çelikleri, metaller arası bileşiklerin çökelme yoluyla güçlendirilmesi yoluyla standart östenitik veya martensitik kalitelerden 2 ila 5 kat daha yüksek mukavemet sağlar.
Düşük MOQ
Farklı ihtiyaçları karşılamak için düşük minimum sipariş miktarı sağlayın.
OEM VE ODM
Benzersiz müşteri ihtiyaçlarını karşılamak için özelleştirilmiş ürünler ve tasarım hizmetleri sağlayın.
Yeterli Stok
Hızlı sipariş işleme ve güvenilir ve verimli hizmet sağlayın.
Müşteri Memnuniyeti
Müşteri memnuniyetini merkeze alarak yüksek kaliteli ürünler sunmak.
bu ürünü paylaş
İçindekiler
Maraging Steel C250 Powder, dövülebilirliğini kaybetmeden ultra yüksek mukavemeti ve tokluğu ile dikkat çeken 18% nikel, kobalt ile güçlendirilmiş çelik (C250) alaşımıdır. Maraging çelikleri, metaller arası bileşiklerin çökelme yoluyla güçlendirilmesi yoluyla standart östenitik veya martensitik kalitelerden 2 ila 5 kat daha yüksek mukavemet sağlar.
Maraging steel C250 is supplied in powder form for additive manufacturing techniques like laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF) which allow printing complex geometries directly from digital CAD models. This enables rapid prototyping and production of lightweight, high-performance components for aerospace, automotive, medical, and tooling applications.
Genel Bakış Maraging Çelik C250 Toz
Maraging steel C250 powder has the following properties:
Tablo 1: Overview of Maraging Steel C250 Powder
| Özellikler | Detaylar |
|---|---|
| Temel Malzeme | Iron Nickel Cobalt Alloy |
| Yoğunluk | 8,1 g/cc |
| Partikül Boyut Aralığı | 15-45 mikron |
| Üretim Yöntemi | Gaz Atomizasyonu |
| Temel Özellikler | Ultrahigh strength, Good fracture toughness, Weldability, Hardens during aging heat treatment |
| Yaygın Ticari İsimler | 18Ni300, NS333, X3NiCoMoTi 18-9-5 |
Some key advantages of maraging steel C250 powder include:
- Ultrahigh tensile strength up to 2500 MPa after aging
- Higher elongation than typical stainless steels
- Good fracture toughness compared to high strength alloys
- Softer than precipitation hardening stainless grades in solutionized state for machining
- Lower distortion compared to martensitic steels during heat treatment
- Excellent dimensional stability during aging
- Easily welded in aged or solution treated condition
Maraging steel C250 does have some limitations as well:
- Requires aging treatment to develop full strength
- Relatively high alloy content increases cost
- Susceptible to embrittlement at high temperatures
- Lower hardness than martensitic stainless grades
Tablo 2: Composition of Maraging Steel C250 Powder
| Alaşım Elemanı | Ağırlık % | Rol |
|---|---|---|
| Nikel | 17 – 19% | Phase hardener |
| Kobalt | 8 – 9% | Yağış güçlendirici |
| Molibden | 4.6 – 5.2% | Yağış güçlendirici |
| Titanyum | 0.6 – 0.8% | Yağış güçlendirici |
| Alüminyum | 0.05 – 0.15% | Deoksidizer |
| Manganez | 0 – 0.1% | Deoksidizer |
| Karbon | < 0.03% | Deoksidizer |
| Demir | Denge | Ana metal |
This composition creates a metastable martensitic matrix after solution annealing which allows for significant secondary hardening by homogeneous precipitation of intermetallic phases during the aging treatment.
Tablo 3: Key Properties of Maraging Steel C250 Powder
| Özellikler | Maraging Steel C250 |
|---|---|
| Yoğunluk | 8,1 g/cc |
| Erime Noktası | 1450°C |
| Elastisite Modülü | 180-210 GPa |
| Elektriksel Dirençlilik | 0.7 microOhm-cm |
| Termal İletkenlik | 16 W/m-K |
| CTE | 10-11 x 10<sup>-6</sup>/K |
| Poisson Oranı | 0.3 |
Uygulamaları Maraging Çelik C250 Toz
Maraging steel C250 powder has found usage across industries in the following applications due to its ultrahigh strength, fracture toughness, and thermal stability:
Havacılık ve Uzay Uygulamaları
- Turbine engine components like discs, shafts, fasteners
- Yapısal gövde bileşenleri
- Roket motoru gövdeleri
- Aerospace fasteners, valves, fittings
Otomotiv Uygulamaları
- Motorsport powertrain parts like connecting rods, shafts
- High performance suspensions, chassis
- Dies, tooling
Endüstriyel Uygulamalar
- Plastik enjeksiyon kalıpları
- Extrusion dies for pipes, tubes
- Blow molds
- Forging, stamping dies
- Grippers, end-effectors for robots
Tablo 4: Specifications, Grades, and Standards for Maraging Steel C250
| Şartname | Sınıf | Standart |
|---|---|---|
| MIL-S-46850D | X3NiCoMoTi18-9-5 | UNS K94530 |
| AMS 6514D | 300 | DIN 1.2709 |
| AMS 6512 | – | – |
| ISO 683/13 | Z 300 | – |
| – | NS333 | – |
Tablo 5: Suppliers and Pricing for Maraging Steel C250 Powder
| Tedarikçi | Ürün Adı | Parçacık Boyutu | Kg başına fiyat |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPW Teknoloji | C250 Maraging Steel | 15-45 μm | $165 |
| Marangoz Toz Ürünleri | Remanium C250 | 15-45 μm | $155 |
| Sandvik Osprey | MARAGE 300 | 15-53 μm | $175 |
| Praxair | C250 Powder | 10-45 μm | $149 |
Heat Treatment of Maraging Steel C250
Maraging steels are supplied in the annealed and descaled condition. A specific heat treatment procedure consisting of solution annealing followed by aging enables maraging steel C250 to attain its ultrahigh strength:
Çözelti Tavlaması
The first step is a homogenizing solution anneal typically done at 820°C ± 15°C for 1-3 hours followed by immediate cooling to room temperature. This renders the material soft but transforms the microstructure into a metastable martensitic matrix through slow cooling to prevent other equilibrium phases like ferrite or cementite from forming.
Yaşlanma
The solutionized maraging steel is then aged at a temperature between 400°C to 500°C for 3-6 hours depending on section thickness. This facilitates diffusion-controlled precipitation of intermetallic compounds like Ni<sub>3</sub>Ti and Fe<sub>2</sub>Mo which obstruct dislocation movement leading to significant strengthening.
Prolonged exposure at higher aging temperatures can compromise properties while insufficient temperature or time will prevent full hardening.
Tablo 6: Typical heat treatment process for maraging steel C250
| Adım | Sıcaklık | Zaman | Cooling Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Çözelti Tavlaması | 820°C ± 15°C | 1-3 hours | Hava soğutmalı |
| Şartlandırma | 350°C – 400°C | 1-3 hours | Hava soğutmalı |
| Yaşlanma | 450°C – 500°C | 3-6 hours | Hava soğutmalı |
The properties achieved after aging treatment are listed below:
Tablo 7: Mechanical properties after aging treatment
| Özellikler | Maraging Steel C250 |
|---|---|
| Çekme Dayanımı | 2465 – 2535 MPa |
| Akma Dayanımı | 2275 – 2345 MPa |
| Uzama | 8 – 10 % |
| Alan Azaltımı | 25 – 30 % |
| Sertlik | 50 – 52 HRC |
| Charpy Impact Energy | 75 – 100 J |
Induction Hardening: For certain components like shafts, gears and fasteners that require enhanced wear-resistance, additional surface hardening by induction heat treatment can be performed after aging to achieve hardness above 50 HRC up to a depth of 2 mm without affecting core properties.
Microstructure of Maraging Steel C250
The microstructure of maraging steel C250 consists of:
Martensitic Matrix: The matrix is predominantly martensite with fine-grained lath morphology produced by quenching after solution annealing. This metastable structure provides sufficient carbon and alloying elements in solid solution for precipitation during aging.
Intermetallic Precipitates: Spherical nano-scale precipitates of Ni<sub>3</sub>Mo and Ni<sub>3</sub>Ti phases dispersed uniformly through the matrix reaching peak volume fractions after full aging treatment. These coherent precipitates pin dislocation movement leading to drastic strengthening.
Carbides and Nitrides: Tiny cubic particles rich in titanium, molybdenum and iron carbides/nitrides may also emerge but comprise < 5% volume fraction.
The combination of tempered martensite matrix and fine dispersion of intermetallic precipitates enables the outstanding strength and toughness that maraging steels exhibit.
Printing Parameters for Maraging Çelik C250 Toz
Machine and Settings
- Machine: Selective laser melting systems like EOS M290, Renishaw AM250, Concept Laser M2
- Layer Thickness: 20-50 μm
- Laser Power: 195-400 W
- Scan Speed: 600-1200 mm/s
- Beam Diameter: 70-100 μm
- Hatch Spacing: 80-120 μm
- Shielding Gas: Argon
- Oxygen Content: <0.1%
Süreçle İlgili Hususlar
- Low residual stress and easier scalability compared to martensitic steels
- Moderate laser energies needed due to lower reflectivity than stainless steel
- Part orientation is optimized to minimize support structures
- 100% dense parts >99.5% can be printed without cracks or porosity defects
- No additional heat treatment needed post SLM processing
- Minor allowances are kept for finish machining after printing
Tablo 8: Properties achieved with additive manufacturing
| Özellikler | Menzil |
|---|---|
| Yoğunluk | >99,5% |
| Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü | Up to 12 μm Ra |
| Çekme Dayanımı | 2300-2500 MPa |
| Akma Dayanımı | 2100-2300 MPa |
| Kopma uzaması | 3-10% |
With optimal parameters, fully dense maraging steel C250 components matching conventional properties can be fabricated by powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. This facilitates complex, lightweight designs unattainable by casting or machining.
Artıları ve Eksileri Maraging Çelik C250 Toz
Tablo 9: Advantages and Limitations of Maraging Steel C250 Powder
| Avantajlar | Sınırlamalar |
|---|---|
| Ultrahigh strength up to 2500 MPa | Cost is higher than carbon steels |
| Retains toughness and ductility after aging | Requires heat treatment to develop full properties |
| Low distortion during heat treatment | Lower wear resistance than martensitic stainless steels |
| Smaller lightweight components enabled | Limited high temperature capability up to 300-400°C |
| Excellent dimensional stability | Susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement over time |
| Good weldability in all conditions |
SSS
Q: What is maraging steel used for?
A: Maraging steels are primarily used in aerospace, motorsports, tooling, and molds where ultrahigh strength, fracture toughness and thermal stability are critical for performance and durability.
Q: Is maraging steel corrosion resistant?
A: While less resistant than stainless grades, maraging steel offers moderately good corrosion resistance comparable to low alloy steels which can be further improved by nickel or chrome plating.
Q: What is the difference between maraging and martensitic steels?
A: Maraging steels use nickel, cobalt, molybdenum alloys to precipitate intermetallic compounds, avoiding C-based martensitic transformation for strengthening. This gives superior mechanical properties.
Q: Does maraging steel need to be quenched?
A: No. Maraging steel is cooled in air after solutionizing to form soft martensite which is later aged to induce precipitation hardening. Quench cracking is avoided.
Q: Is maraging steel magnetic?
A: Yes, maraging steel in all conditions displays ferromagnetic behavior due to its iron-based austenitic matrix. Nickel content is not high enough to become paramagnetic.
Q: What is the difference between Grade 300, 350 and C250 maraging steel?
A: The grades denote yield strength levels after aging. C250 implies a minimum yield strength of 1880 MPa or 250 ksi while Grade 300 and 350 maraging steels are specified for minimum yield strengths of 2050 MPa and 2415 MPa respectively.
Son Fiyat Alın
Met3DP Hakkında
Ürün Kategorisi
SICAK SATIŞ
BİZE ULAŞIN
Herhangi bir sorunuz var mı? Bize şimdi mesaj gönderin! Mesajınızı aldıktan sonra tüm ekibimizle talebinize hizmet edeceğiz.