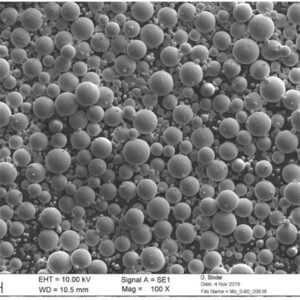
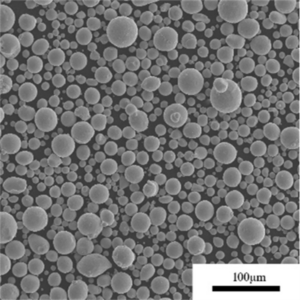
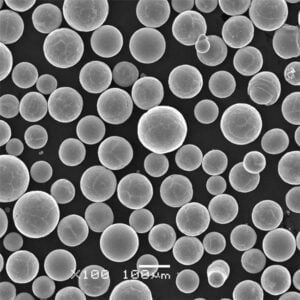
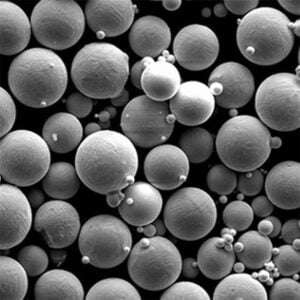
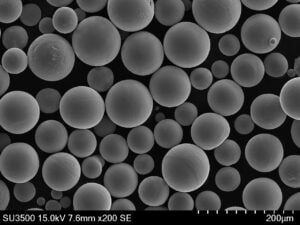
Overview
Titanium powder is a versatile metallic material valued for its unique combination of high strength, low density, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. As a powder, titanium facilitates advanced manufacturing techniques like metal injection molding (MIM), additive manufacturing (AM), hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and powder metallurgy (PM) pressing and sintering to create complex titanium components.
Key applications for titanium powder include aerospace components, medical implants, automotive parts, sporting equipment, chemical processing, and consumer products. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of titanium powder, including production methods, alloy compositions, characteristics, properties, specifications, applications, and global suppliers. It aims to assist engineers, product designers, and technical program managers in selecting and using titanium powders.

Production of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is produced using the following primary methods:
Titanium Powder Production Methods
- Gas Atomization – High pressure inert gas disintegrates molten titanium into spherical powder
- Plasma Atomization – Titanium electrode arcs create ultrafine spherical powder
- Hydriding/Dehydriding – Titanium hydride powder (TiO2) is dehydrided into fine powders
- Mechanical Milling – Ball milling breaks down titanium chips into irregular particles
- Plasma Spheroidization – Irregular powder melted in plasma to produce spherical shapes
Gas atomization and mechanical milling are most common, creating spherical and angular powder shapes respectively. Additional screening, conditioning, and blending create application-specific particle size distributions.
Compositions of Titanium Powder
While commercially pure titanium powders are available, most powders for industrial uses contain small amounts of alloying elements:
Common Titanium Powder Compositions
| Alloy | Primary Alloying Elements | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| CP Titanium | 99.5%+ Ti | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 6% Al, 4% V | High strength, heat treatable |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | 6% Al, 7% Nb | High strength, biocompatible |
| Ti-555 | 5% Al, 5% Mo, 5% V | Heat treatable, machinable |
| Ti-1023 | 10% V, 2% Fe, 3% Al | High strength, good ductility |
Aluminum, vanadium, and niobium are common additions to enhance strength and workability. Trace boron, carbon, iron, and oxygen also appear.
Alloying tailors microstructure, hardness, machinability, and other properties while retaining excellent corrosion resistance.
Characteristics of Titanium Powders
Key characteristics of titanium powder include:
Titanium Powder Characteristics
| Characteristic | Typical Values | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 10 – 150 microns | Sintering behavior, surface finish |
| Particle shape | Spherical, angular, dendritic | Powder flow and packing density |
| Apparent density | 1.5 – 4.0 g/cc | Pressing and handling behavior |
| Tap density | 2.5 – 4.5 g/cc | Indicator of compressibility |
| Hall flow rate | 25 – 35 s/50g | Powder flowability |
| Loss on ignition | 0.1 – 0.5 wt% | Oxygen and moisture content |
| Pyrophoricity | None | Flammability and handling precautions |
Particle size distribution and powder shape significantly impact powder flow, compaction, sintering response, and density of pressed and sintered parts. Apparent density indicates powder compressibility.
Properties of Titanium Powders
Key titanium powder properties include:
Titanium Powder Properties
| Property | Pure Ti | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-6Al-7Nb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cc | 4.43 g/cc | 4.52 g/cc |
| Tensile Strength | 240 MPa | 930 MPa | 900 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 170 MPa | 860 MPa | 825 MPa |
| Elongation | 24% | 10% | 15% |
| Elastic Modulus | 102 GPa | 114 GPa | 105 GPa |
| Hardness | 80 HB | 334 HB | 321 HB |
| Heat Capacity | 522 J/kg·K | 526 J/kg·K | 527 J/kg·K |
| Thermal Conductivity | 7.2 W/m·K | 7.2 W/m·K | 6.7 W/m·K |
Alloying with aluminum, vanadium, and niobium enhances strength and hardness significantly. Specific properties depend heavily on final microstructure.
Applications of Titanium Powder
Key applications for titanium powder include:
Titanium Powder Applications
| Industry | Uses | Key Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Structural components, turbine blades, fasteners | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Medical | Orthopedic implants, dental implants, surgical tools | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Connecting rods, valves, springs, fasteners | Light weighting, performance |
| Chemical | Tanks, pipes, valves, pumps | Corrosion resistance |
| Sporting goods | Golf clubs, bicycles, helmets | Strength, tailored mechanical properties |
| Petrochemical | Downhole tools, wellhead parts | Strength, corrosion resistance |
Titanium’s unique properties make it attractive for reducing weight in aerospace components while maintaining mechanical integrity in extreme environments.
Excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance drive usage in orthopedic and dental implants. The ability to tailor titanium’s properties facilitates sporting goods with specialized performance characteristics.
Specifications for Titanium Powders
Titanium powder compositions and quality are defined by various standard specifications:
Titanium Powder Standards
| Standard | Scope | Particle Size | Purity | Chemistry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM B348 | Grade 1-4 unalloyed Ti powder | -635 mesh | 99.5%, 99.9%, 99.95% Ti | O, C, N, H limits |
| ASTM B801 | Ti-6Al-4V alloy powder | -635 mesh | Ti, Al, V composition ranges | Interstitial limits |
| ISO 23301 | Additive manufacturing Ti powder | 10-45 microns | 99.5%+ Ti | O, N, C, H, Fe limits |
| AMS 4992 | Aerospace grade Ti-6Al-4V powder | -150 mesh | Ti, Al, V composition ranges | Interstitial limits |
These define acceptable levels of alloying additions, impurities like oxygen/nitrogen/carbon, particle size distributions, and other test methods relevant for different applications.
Global Suppliers of Titanium Powders
Many major corporations produce titanium powders along with smaller regional manufacturers:
Titanium Powder Manufacturers
| Supplier | Production Methods | Materials | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATI Metals | Gas atomization | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-1023, pure Ti | Wide alloy range, large volumes |
| Praxair | Gas atomization | Ti-6Al-4V, CP Ti | Small lots, rapid delivery |
| Carpenter Additive | Gas atomization, hydride-dehydride | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, pure Ti | Custom alloys, small lots |
| AP&C | Plasma atomization | CP Ti, Ti alloys | Ultrafine 10-45 micron powder |
| Tekna | Plasma spheroidization | Ti-6Al-4V, CP Ti | Convert chips into spherical powder |
| Baoji Hanz Titanium | Hydriding | CP Ti, Ti-6Al-4V | Low costChinese producer |
Many supply both standard and custom alloy compositions. Some provide toll processing of scrap and chips into powder.
Selecting Titanium Powder
Key considerations for selecting titanium powder include:
- Alloy composition – Balances desired properties like strength, ductility, hardness
- Purity level – Affects mechanical properties and microstructure
- Particle size and shape – Influences powder flow, density, surface finish
- Apparent and tap density – Indicates compressibility and sintering response
- Chemical compatibility – For service conditions like acids or salt water
- Sampling procedures – Representative testing of powder lots
- Quality certifications – ISO 9001, AS9100, etc.
- Technical expertise from powder producer
Samples builds and prototypes help qualify new alloys and powders for a given application. Work closely with reputable suppliers to obtain well-characterized titanium powder for optimal results.

FAQ
What is the benefit of plasma atomized titanium powder?
Plasma atomization produces very spherical, flowing particles typically 10-45 microns in size. This allows excellent sintered density and surface finish.
What causes titanium powder to be pyrophoric?
Pyrophoric titanium powders ignite spontaneously in air. This is caused by extremely small particle sizes below 10 microns which greatly increase surface area and reactivity. Use inert gas handling for pyrophoric powders.
How does particle shape influence titanium powder properties?
Spherical powder flows well and provides higher and more uniform density and mechanical properties. Irregular powder offers better green strength and compressibility but less predictable shrinkage.
What post-processing can improve titanium powder reuse?
Screening, milling, and thermal treatments allow reuse of off-spec powders. Plasma spheroidization converts chips and coarser particles into spherical powder feedstock.
What standards apply to additive manufacturing of titanium parts?
ASTM F3001-14 covers characterization and quality control of Ti alloy powder for AM. ASTM F2924-14 gives standard test methods for evaluating mechanical properties of AM titanium.
Can you 3D print a titanium and steel composite structure?
Yes, some metal 3D printing processes transition between titanium and stainless steel alloys within one part by precise material switching to build bimetallic components.
Conclusion
Titanium powder provides engineers great flexibility to build high performance components thanks to the metal’s unique properties. Careful selection of powder characteristics and close collaboration with experienced suppliers enables optimal results across many critical applications. Ongoing advances continue to expand the capabilities, quality, and cost-effectiveness of titanium powder metallurgy processes.