Overview
Titanium metal powder is a fine granular form of titanium metal used in various manufacturing applications. It offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility making it suitable for use in aerospace components, medical implants, sports equipment, automotive parts, and more.
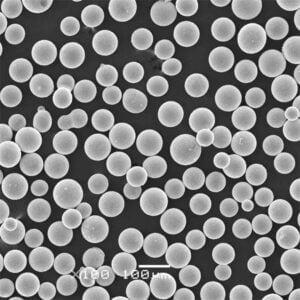
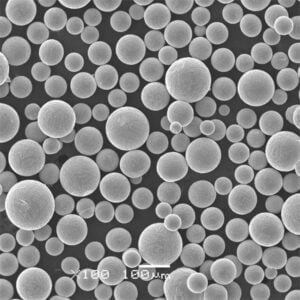
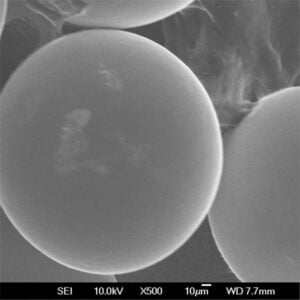
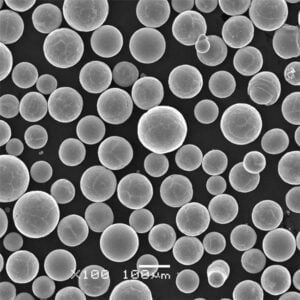
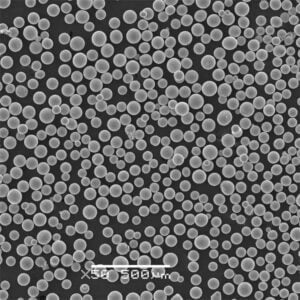
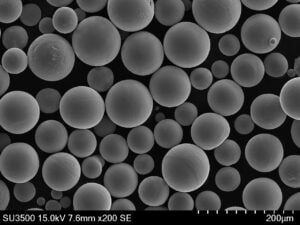
Titanium powder can be produced through different methods including atomization of molten titanium, electrolysis of titanium compounds, and direct reduction of titanium ores. The properties and performance of the powder depends on the production technique as well as post-processing treatments. Critical characteristics that define the quality and usability of titanium powder include particle size distribution, morphology, powder flowability, apparent density, and impurity levels.

Types of Titanium Metal Powder
| Type | Production Method | Particle Size | Morphology | Apparent Density | Flowability | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomized | Gas or plasma atomization of molten titanium | 10 – 250 μm | Spherical, granular | 2.2 – 3.8 g/cc | Good | Additive manufacturing, MIM |
| Hydride-dehydride (HDH) | Hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of titanium scrap | <250 μm | Irregular, spongy | 1 – 2.5 g/cc | Poor | Metal injection molding |
| Rotating electrode process | Electrolysis of titanium compounds | 5 – 150 μm | Dendritic | 2 – 3 g/cc | Fair | Additive manufacturing |
| Aluminothermic reduction | Chemical reduction with aluminum | 50 – 500 μm | Irregular, porous | 1.5 – 3 g/cc | Fair | Refractory metallisation |
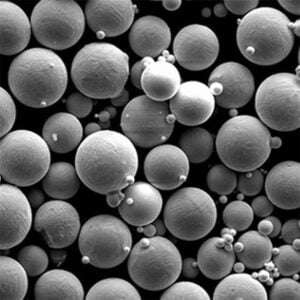
Atomized titanium powder is spherical in morphology with good flow and packing characteristics. It is suitable for demanding additive manufacturing and metal injection molding applications.
Hydride-dehydride powder has lower density and poor flow compared to atomized powder. It is used predominantly for metal injection molding due to its lower cost.
Rotating electrode process powder has unique dendritic particles providing high sintered density. It is used in additive manufacturing methods like electron beam melting.
Composition of Titanium Metal Powder
Titanium metal powders are broadly categorized into four grades based on oxygen and iron content as per ASTM standards:
| Grade | Oxygen (wt%) | Iron (wt%) | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 0.18 | 0.20 | N, C, H |
| Grade 2 | 0.25 | 0.30 | N, C, H |
| Grade 3 | 0.35 | 0.30 | N, C, H |
| Grade 4 | 0.40 | 0.50 | N, C, H |
The main alloying elements in titanium powder include:
- Aluminum (Al) – Improves strength and heat treatability
- Vanadium (V) – Increases strength and ductility
- Tin (Sn) – Improves creep resistance
- Zirconium (Zr) – Refines grains
Trace elements like nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and iron also have significant effects on mechanical properties. Strict control over chemical composition is necessary to achieve optimal performance.
Properties of Titanium Metal Powder
| Property | Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3 | Lower than steel and nickel alloys |
| Melting point | 1660°C | Retains strength at high temperatures |
| Strength | 900 – 1200 MPa | Stronger than aluminum |
| Elastic modulus | 100 – 120 GPa | Lower modulus than steel |
| Elongation | 15 – 25% | Good ductility |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Due to protective oxide layer |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | Suitable for medical implants |
| Thermal conductivity | 7 – 16 W/m.K | Lower than aluminum and steel |
The properties of finished titanium components depend on the powder characteristics as well as how the parts are manufactured. Porosity, surface finish, heat treatment, etc. have a large influence.
Key advantages of titanium metal include high specific strength, corrosion resistance, fatigue life, and biocompatibility. Limitations include high reactivity at elevated temperatures requiring inert atmospheres for powder handling and processing. Titanium alloys can also be more difficult to machine compared to other metals due to low thermal conductivity causing localized heating during machining.
Applications of Titanium Metal Powder
| Application | Examples | Required Powder Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | Aerospace components, orthopedic implants | Spherical morphology, controlled particle size distribution below 100 μm, high purity |
| Metal injection molding | Dental implants, fasteners | Irregular powder below 25 μm suitable for binder mixing |
| Refractory metallisation | Titanium coatings on metal substrates | Wide range of powder sizes from 5 μm to 500 μm |
| Powder metallurgy | Connecting rods, drive shafts | Tight control over oxygen and nitrogen content, good compressibility and sinterability |
| Thermal spray coatings | Protective coatings for marine applications | Special plasma spray grade powder with optimized particle size distribution |
| Pyrotechnics | Flares, explosives | Coarser powder above 150 μm suitable for metal fuel formulations |
Fine powders below 100 microns are preferred for additive manufacturing to achieve good resolution and mechanical properties. For pressed and sintered applications, spherical morphology provides optimal density whereas irregular particles are preferred for metal injection molding feedstocks.
Specifications for Titanium Metal Powder
ASTM standards for different titanium powder grades:
| Standard | Description | Grades Covered |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B849 | Standard for prealloyed titanium powder for MIM | Grade 1 to 4 |
| ASTM B981 | Standard for titanium alloys for thermal spray coatings | Grade 1 and 2 |
| ASTM B983 | Standard for titanium hydride-dehydride powder for MIM | Grade 1 to 4 |
Other titanium powder specifications:
| Parameter | Typical Values | Test Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | 10 μm to 150 μm | Laser diffraction, sieve analysis |
| Apparent density | 1 to 4 g/cc | Hall flowmeter, Scott volumeter |
| Tap density | 70 to 80% of true solid density | ASTM B527 |
| Powder morphology | Spherical, granular, sponge, dendritic | SEM, optical microscopy |
| Flow rate | 25 to 35 s/50 g | Hall flowmeter |
| Loss on ignition | 0.1 to 2 wt% | ASTM E1019 |
| Residual hydrogen | 100 to 500 ppm | LECO inert gas fusion |
Suppliers of Titanium Metal Powder
| Supplier | Production Method | Powder Grade | Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP&C | Plasma atomization | Grade 1, 2, 5 | 10 to 45 μm |
| TLS Technik | Gas atomization | Grade 23 | 45 to 150 μm |
| AMETEK | Rotating electrode | Grade 2 | 5 to 63 μm |
| Puris | Hydride-dehydride | Grade 2 | Up to 150 μm |
Indicative pricing for titanium metal powder:
| Grade | Pricing ($/kg) |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 50 to 150 |
| Grade 2 | 40 to 100 |
| Grade 5 | 250 to 500 |
Bulk discounts may be available for large orders above 100 kg. Actual pricing varies based on quantity, quality requirements, lead time, etc.
Comparison of Titanium Powder Production Methods
| Parameter | Gas Atomization | Plasma Atomization | HDH Process | Rotating Electrode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Granular, spherical | Highly spherical | Sponge, irregular | Dendritic |
| Oxygen Pickup | Moderate | Low | High | Low |
| Throughput | Moderate | Low | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | AM, MIM | AM, aerospace | MIM | AM |
No single production method offers the best balance of quality and economics. Most manufacturers specialize in one technology and offer different grades targeting various applications. Powder quality and repeatability is critical for demanding applications whereas cost is a larger driving factor for high volume products.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between titanium grades 1, 2, 3 and 4 powder?
A: The grades differ based on the allowed oxygen and iron content. Grade 1 has the lowest oxygen levels whereas grade 4 permits higher impurity levels. Lower grades provide superior mechanical properties while higher grades reduce cost.
Q: What particle size titanium powder do I need for additive manufacturing?
A: For most AM processes, the optimal particle size range is 10 to 45 microns. Finer powders below 100Copy microns enable good resolution and mechanical properties. However, extremely fine particles below 10 μm can be challenging to spread evenly during layering. They are also more prone to agglomeration issues.
Q: Is titanium powder hazardous?
A: Titanium powder can ignite and cause explosion hazards under certain conditions. Fine titanium powders, especially hydride powders, are highly flammable. Handling titanium powder requires inert gas environments using argon or nitrogen. Storage containers should have proper grounding. Workers must take precautions against dust inhalation and skin contact when handling titanium powders.
Q: How is titanium powder produced?
A: The four main production methods are:
- Gas atomization: Molten titanium stream is broken into droplets which solidify into powder
- Plasma atomization: Extremely high heat from plasma rapidly melts and solidifies titanium
- HDH process: Titanium scrap is processed using hydrogen cycles of absorption and desorption
- Rotating electrode: Anodic dissolution of titanium rods forms powder through electrolytic reactions
Each process results in powder with different characteristics suited to various applications.
Q: What is the price of titanium powder?
A: Titanium powder can range from $40 to $500 per kg based on grade, quality, order volume, etc. Spherical grades 1 and 2 powder are moderately priced around $100/kg for small quantities. Special alloys used in aerospace can cost up to $500/kg. Hydride-dehydride and higher grade 4 powder are cheaper options closer to $50/kg for industry buyers.