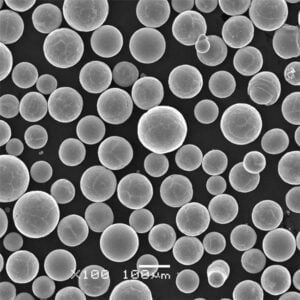
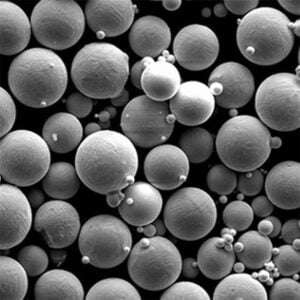
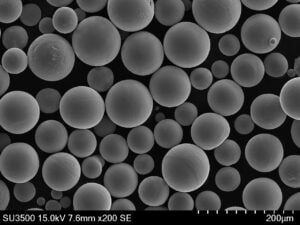
Overview of Atomized Metal Powders
atomizing metal powder industry are essential raw materials for industrial applications like metal 3D printing, thermal spray, metal injection molding, brazing, and welding.
Key attributes of atomized metal powders:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Production method | Gas or water atomization to make fine droplets |
| Materials | Alloys of aluminum, titanium, nickel, cobalt, stainless steel |
| Particle shape | Spherical or irregular morphology |
| Particle size | From 10 microns to 150+ microns |
| Size distribution | Tight control of particle size ranges |
Precise control over powder characteristics allows tailoring to specific application requirements in terms of composition, size, shape, and quality.
Applications for Atomized Metal Powders
The major applications for atomized metal powders include:
| Application | Typical Materials Used |
|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | Ti, Al, Ni, stainless, Co alloys |
| Metal injection molding | Stainless, Ti, alloy steels |
| Thermal spray | Cu, Al, Ni, stainless |
| Brazing and soldering | Cu, Ag, Ni alloys |
| Welding | Al, stainless, Ni alloys |
The spherical morphology and tight size control achievable with atomization makes the powders ideal for these processes.
Specialized characteristics like flowability, apparent density, and purity can be tailored to meet the requirements of each application through careful control of the atomization process parameters and conditions.

Methods of Producing Atomized Metal Powders
The main methods of producing atomized metal powders are:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | Melted metal is disintegrated by high pressure gas jets into fine droplets. |
| Water atomization | Molten metal stream is shattered into droplets by high velocity water. |
| Rotating electrode | Centrifugal forces disperse molten metal off spinning electrodes. |
| Plasma atomization | Plasma arc melts wire feedstock into ultrafine powder. |
Each method can produce powders with unique characteristics suited to different applications. Gas atomization is the most widely used process industrially.
atomizing metal powder industry Production Process
A typical gas atomization metal powder production process involves:
- Raw material preparation – Melting ingots and alloying
- Atomization – Disintegration of metal into powder
- Powder collection – Separation from atomizing gas
- Sieving – Classifying powder into size fractions
- Conditioning – Flow additives, drying, blending
- Quality control – Sampling and testing to specifications
- Packaging – Canisters, bottles, drums for shipment
Careful process control at each step ensures repeatable powder quality and characteristics. The process takes place using automated, industrial-scale equipment.
Design and Operation of Gas Atomizers
Gas atomizers utilize the following key design elements:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Pressure vessel | Holds inert gas at elevated pressure |
| Nozzles | Accelerate pressurized gas to supersonic speeds |
| Melt pouring system | Delivers molten metal stream into atomizing area |
| Cyclones and filters | Separate powder from gas flow |
| Control system | Monitors and regulates process parameters |
In operation, the metal melt is poured into high velocity inert gas jets that disintegrate it into fine powder. The powder characteristics are controlled by parameters like gas pressure, nozzle design, pour rate, and melt superheat.
Key Quality Attributes of Atomized Metal Powders
Important quality attributes for atomized powders:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle size range | Controlled distribution focusing on critical sizes |
| Morphology | Spherical/rounded preferred over irregular shapes |
| Chemical composition | Tight control of alloying elements in each batch |
| Apparent density | Higher densities improve product performance |
| Impurities | Minimizing gaseous pickup (e.g. oxygen) |
| Flow characteristics | Smooth powder flow without agglomeration |
Meeting application specifications requires tight control and monitoring of quality at each step of manufacturing.
Considerations for Gas Atomization Process Scaling
Key factors when scaling up gas atomization production:
- Larger batches increase melt inventory requirements
- Retaining stable melt stream at higher flows critical
- Increased gas use must be accommodated
- Larger sieving systems for higher powder volumes
- Expanded material handling and storage areas
- Upgrade control systems and data acquisition
- Personnel training on larger equipment
Benefits of larger scale production include improved productivity, flexibility, and economy of scale.
Specifications for Metal Powders in AM
Typical powder specifications for additive manufacturing applications:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Particle size | 10-45 microns common |
| Morphology | Spherical, smooth surface |
| Composition | Tight control of alloying elements |
| Apparent density | > 4 g/cc desired |
| Flowability | Excellent flow, no agglomeration |
| Impurities | Minimized oxygen preferred |
Meeting performance requirements for AM powders demands strict composition, size, and morphology control during atomization.
Powder Characterization Methods
Important methods for analyzing atomized metal powders:
| Method | Data Provided |
|---|---|
| Sieving | Particle size distribution |
| Hall flowmeter | Powder flow rates |
| Optical microscopy | Morphology and microstructure |
| SEM imaging | High magnification morphology |
| Apparent density | Packing density of powder |
| Chemical analysis | Composition of elements |
Data from testing helps correlate powder characteristics to performance in downstream applications.
Global Metal Powder Market Size
The global metal powder market size:
- Valued at $2.9 billion in 2020
- Projected to reach $5.7 billion by 2028
- Compound annual growth around 10%
Key growth drivers:
| Factor | Influence on Growth |
|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | Rapid growth in demand for metal AM powders |
| Lightweighting trends | Increased use of powders for light alloys |
| High performance parts | Powders enable advanced alloy parts |
| Electric vehicles | New powders developed for motors/batteries |
The market is projected for strong continued growth as powders enable advanced manufacturing techniques across industries.
Economic Benefits of Metal Powder Production
Economic impacts of metal powder production:
- Generates high value advanced materials from raw metals
- Creates specialized, high wage manufacturing jobs
- Metal powders are exported globally from producing regions
- Enables downstream manufacturing technologies and products
- Significant capital investment required for production facilities
- Rising demand increases economic activity and investments
The sector has upstream and downstream impacts across supply chains and manufacturing.
Leading Regions for Metal Powder Production
Major metal powder producing regions globally:
| Region | Key Details |
|---|---|
| North America | USA is largest producer globally, exports significant volumes overseas |
| Europe | Major producers in Germany, Sweden, UK serving European industries |
| Asia Pacific | China, India, South Korea are major producers focused on domestic use |
| Middle East | Growing production driven by aerospace and oil/gas industries |
Proximity to end-use industries and high domestic demand drive localized growth. Exports also serve global regions.
Metal Powder Industry Growth Drivers
Major drivers spurring growth in the metal powder industry:
| Driver | Growth Effects |
|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | Surging demand for specialized AM metal powders |
| Lightweighting | Replacement of solid metal with powders |
| High strength alloys | New powder alloys for strong lightweight parts |
| Electric vehicles | Powder-based motors, batteries |
| Aerospace | Powder-based parts for engines, airframes |
These technology trends are spurring investment and expansion in metal powder production capacity.
Metal Powder Industry Challenges
Key challenges facing the metal powder industry:
| Challenge | Effects |
|---|---|
| High capital costs | Restrains new entrants and investments |
| Raw material prices | Feedstock price volatility impacts costs |
| Quality requirements | Testing and process control expenses |
| Safety regulations | Explosion risks drive compliance costs |
| Consolidation | acquisitions decrease competition |
These factors make growth and sustainability challenging despite strong market demand. Companies must innovate to remain competitive.
Technology Trends in Metal Powder Production
Emerging technology trends in metal powder manufacturing:
- Additive manufacturing of atomization equipment components for design flexibility
- Power ultrasound assisted atomization for finer powders
- Advanced modeling of fluid dynamics and powder formation
- Increased automation and process monitoring via sensors
- Machine learning for predictive quality control
- Direct reuse of powders in closed-loop additive manufacturing
- Novel gas atomization methods for micro-nano powder production
- Specialized alloy development for emerging applications
Technology innovations will enable greater powder quality and consistency at higher production volumes to meet accelerating market growth.

Summary of the Metal Powder Industry Landscape
- Critical provider of powders for major manufacturing industries
- Gas atomization is dominant production technology
- Demand growing rapidly driven by high performance alloys
- High barriers to entry but strong future outlook
- Quality control and advanced processing key capabilities
- Developing alongside metal additive manufacturing
- High-wage manufacturing sector with regional production hubs
- Poised for continued expansion and technology development
Atomized metal powders will only increase in economic importance as a strategic material for advanced metalparts production across critical industries.
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the largest metal powder market globally? | North America, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific regions. |
| What are the main industry applications for metal powders? | Additive manufacturing, thermal spray, metal injection molding are the largest applications. |
| What alloys are commonly atomized into powder? | Aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, nickel, and cobalt alloys are the most common. |
| What is gas atomization used for? | Gas atomization is the leading method for commercial production of metal powders. |
| How are metal powders separated by size? | Sieving/screening is used to classify powders into specific particle size ranges. |