
ブログ
すべてのコレクション


ワイヤーアーク積層造形入門
機械加工のような減法的製造技術ではなく、材料を丹念に加えることによって、大きくて頑丈な金属部品を層ごとに作ることを想像してみてください。この革新的な技術がワイヤーアークアディティブマニュファクチャリング(WAAM)であり、さまざまな産業における重要な部品の製造方法を再構築する準備が整っています。ワイヤーアークアディティブマニュファクチャリング(WAAM)の動作原理、
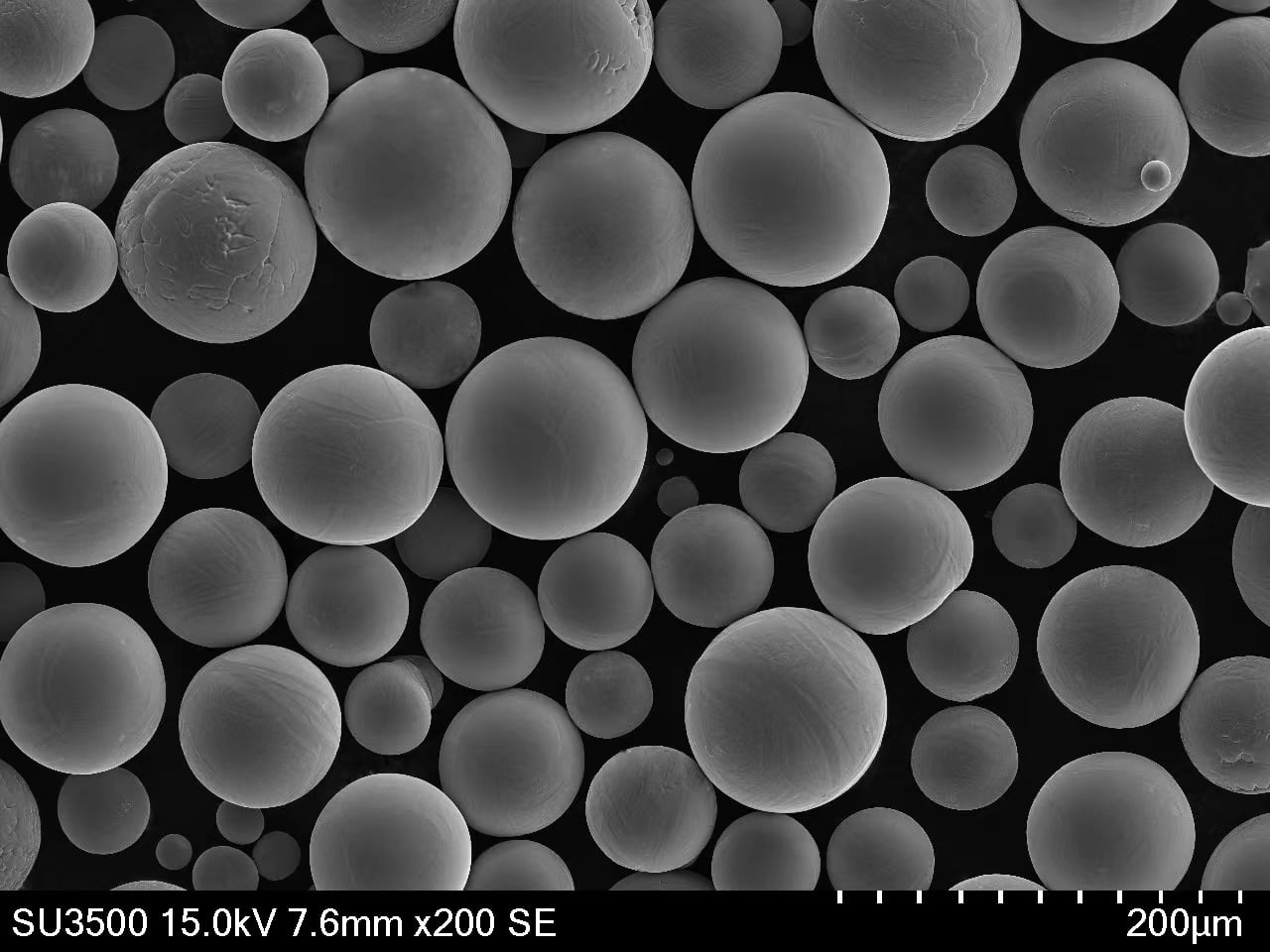
優れた金属粉末のためのプラズマ回転電極プロセス(PREP)
金属部品が伝統的な手段ではなく、小さな完全な球体の金属粒子を用いて一層一層丹念に作り上げられる世界を想像してみてほしい。この未来的なビジョンは、3Dプリンティングとしても知られるアディティブ・マニュファクチャリング(AM)の礎石である。しかし、これらを実現する魔法の成分についてはどうだろう?

材料噴射と指向性エネルギー蒸着の比較
複雑な物体が、魔法ではなく、3Dプリンティングの驚異によって、層ごとに実体化する世界を想像してみてほしい。この領域には、2つの強力な競合が存在する:マテリアルジェットとDED(Directed Energy Deposition)である。どちらも付加製造の原理を利用したものだが、アプローチが異なるため、利点と限界がはっきりしている。つまり

金型や工具の製造にDEDを使用する利点
複雑な金型や工具を、比類のない自由設計、リードタイムの短縮、材料の無駄の最小化で製造できる世界を想像してみてください。これはサイエンス・フィクションではなく、製造業を一変させる画期的な付加製造(AM)技術であるDED(Directed Energy Deposition)が提供する現実だ。DEDはまた

医療分野におけるDEDの応用
損傷した骨を、その人特有の解剖学的構造に合わせて完璧にカスタマイズされたインプラントで修復できる世界を想像してみてほしい。外科医が、複雑な手技のニーズに合わせて層ごとに作られた道具を使う世界を。このような未来は、DED(Directed Energy Deposition)という革新的な技術のおかげで、急速に近づいている。

自動車製造向けDED
The automotive industry is in a constant state of flux, driven by relentless demands for lighter, stronger, and more fuel-efficient vehicles. Enter Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a revolutionary additive manufacturing (AM) technology poised to transform the way cars are built. Imagine a process that builds complex metal parts layer by

航空宇宙分野におけるDEDの応用
Imagine a world where complex aircraft components can be built layer by layer, on-demand, with minimal waste. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) technology rapidly transforming the aerospace industry. DED, also known as Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS), utilizes
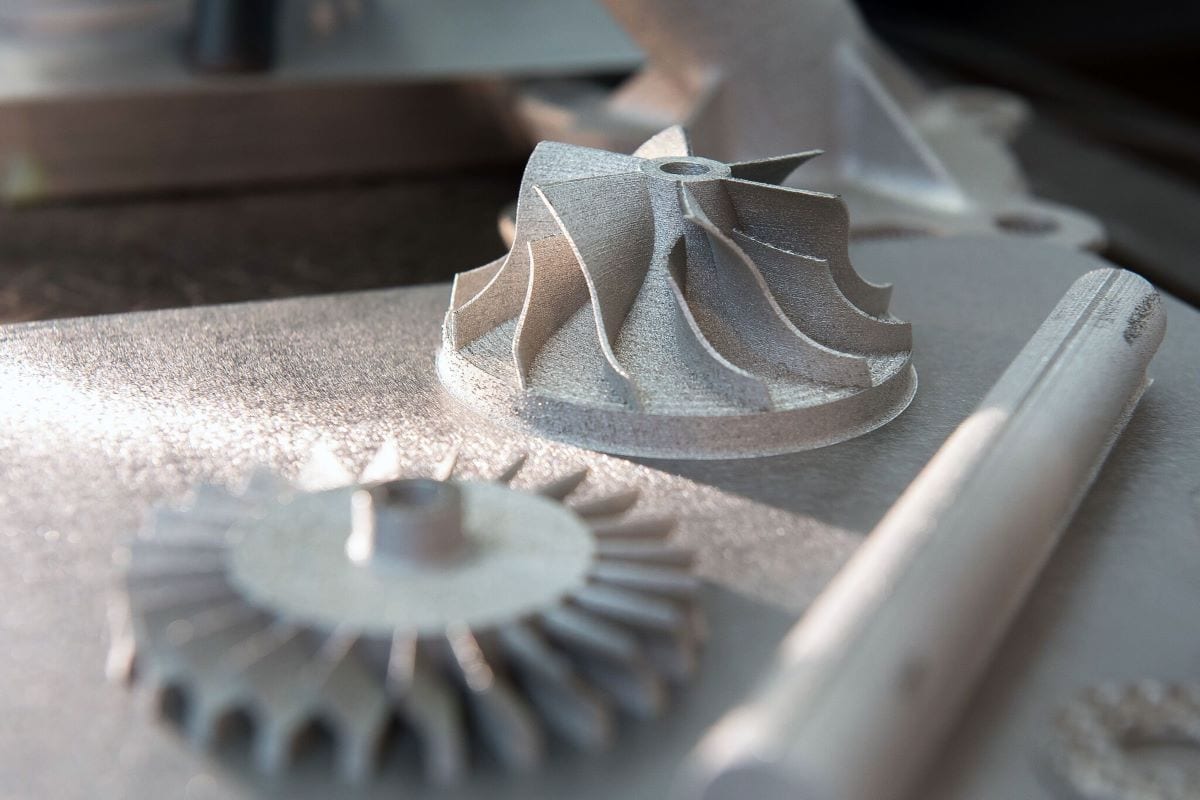

指向性エネルギー蒸着の紹介
Imagine building complex metal structures layer by layer, with precise control over material properties and minimal waste. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a revolutionary 3D printing technology that’s transforming the manufacturing landscape. Directed Energy Deposition, also known by terms like Laser Engineered Net

ラピッドプロトタイピングにおける材料噴射の応用
Imagine a world where crafting intricate prototypes is as seamless as printing a document. Material jetting, a revolutionary 3D printing technology, transforms this vision into reality. By meticulously depositing droplets of photopolymer resin layer by layer, material jetting unlocks a treasure trove of possibilities for rapid prototyping. Buckle up, as

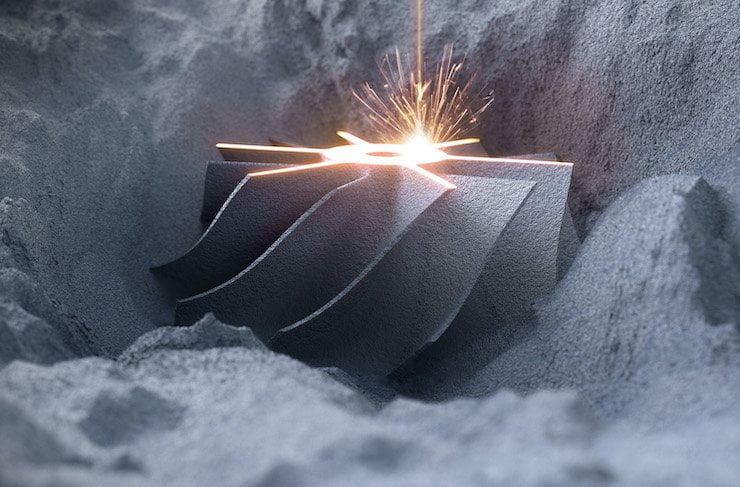
WAAMの作業手順
Imagine building complex metal structures layer by layer, like a culinary master crafting a magnificent cake. That’s the essence of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM), a revolutionary 3D printing technology that’s transforming the way we create metal parts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the captivating world of WAAM, taking you on a journey from

ワイヤーアーク積層造形入門
Imagine building large, robust metal parts layer by layer, not through subtractive manufacturing techniques like machining, but by adding material meticulously. This transformative technology is Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM), poised to reshape how we create critical components across various industries. The Working Principle of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing WAAM, also known as Directed Energy
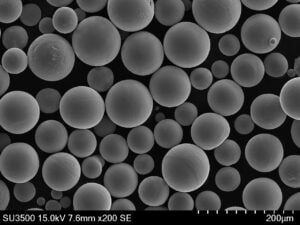
優れた金属粉末のためのプラズマ回転電極プロセス(PREP)
Imagine a world where metal components are crafted not through traditional means, but by meticulously building them layer by layer using tiny, perfectly spherical metal particles. This futuristic vision is the cornerstone of Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing. But what about the magic ingredient that brings these intricate objects to life? Enter

材料噴射と指向性エネルギー蒸着の比較
Imagine a world where complex objects materialize layer by layer, not through magic, but through the marvels of 3D printing. Within this realm exist two powerful contenders: Material Jetting and Directed Energy Deposition (DED). Both utilize additive manufacturing principles, but their approaches diverge, leading to distinct advantages and limitations. So, which champion reigns supreme for

金型や工具の製造にDEDを使用する利点
Imagine a world where complex molds and tools can be built with near-unparalleled freedom of design, reduced lead times, and minimized material waste. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality offered by Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a revolutionary additive manufacturing (AM) technology poised to transform the manufacturing landscape. DED, also known as Laser Metal Deposition

医療分野におけるDEDの応用
Imagine a world where damaged bones can be repaired with implants perfectly customized to fit your unique anatomy. A world where surgeons wield tools built layer-by-layer to match the intricate needs of complex procedures. This future is rapidly approaching, thanks to the innovative technology known as Directed Energy Deposition (DED). DED, also sometimes referred to

自動車製造向けDED
The automotive industry is in a constant state of flux, driven by relentless demands for lighter, stronger, and more fuel-efficient vehicles. Enter Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a revolutionary additive manufacturing (AM) technology poised to transform the way cars are built. Imagine a process that builds complex metal parts layer by layer, offering unparalleled design freedom

航空宇宙分野におけるDEDの応用
Imagine a world where complex aircraft components can be built layer by layer, on-demand, with minimal waste. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) technology rapidly transforming the aerospace industry. DED, also known as Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS), utilizes a focused energy source, like

指向性エネルギー蒸着の紹介
Imagine building complex metal structures layer by layer, with precise control over material properties and minimal waste. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of Directed Energy Deposition (DED), a revolutionary 3D printing technology that’s transforming the manufacturing landscape. Directed Energy Deposition, also known by terms like Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) or Direct Metal

ラピッドプロトタイピングにおける材料噴射の応用
Imagine a world where crafting intricate prototypes is as seamless as printing a document. Material jetting, a revolutionary 3D printing technology, transforms this vision into reality. By meticulously depositing droplets of photopolymer resin layer by layer, material jetting unlocks a treasure trove of possibilities for rapid prototyping. Buckle up, as we delve into the captivating
製品
売れ筋商品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末

