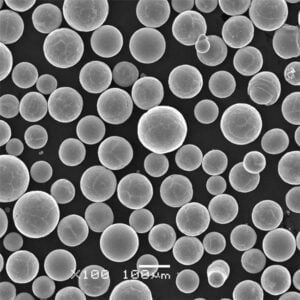
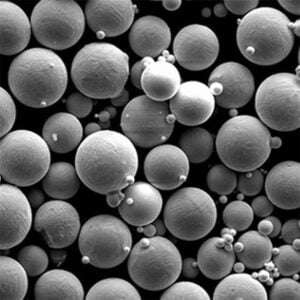
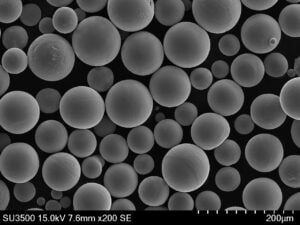
Titanium powder is a key material used across several major industries due to its unique properties like high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. This article provides an overview of titanium powder types, production methods, global supply chains, pricing, and uses across aerospace, medical, automotive, and other sectors.
Overview of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder refers to fine particulate titanium metal used as a feedstock for manufacturing parts and components via powder metallurgy techniques. The small particle size leads to certain advantages over bulk titanium.
Key properties:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Corrosion resistance
- Ability to withstand extreme temperatures
- Biocompatibility
- Allows complex part geometries
Powder specifications:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Purity | Grade 1 through 4 titanium (99.5-99.995% Ti) |
| Particle shape | Spherical, angular, or mixed |
| Particle size | 15-250 microns typically |
| Production method | Atomization, hydride-dehydride, electrolysis |
Grades and alloying elements:
Titanium powder is available in various grades – CP1 through CP4 commercially pure and Ti 6Al-4V grade 5 alloy being the most common. Other alloys contain Mo, Zr, Sn, Si, Cr, Fe, O, Nb, Ta, W to enhance properties.
Common forms:
- Powder – loose bulk form or compressed into tablets
- Wire
- Rod
- Custom parts and components
Titanium’s high reactivity means it cannot be produced via melting and casting methods alone. Advanced powder production and consolidation techniques are essential to harness titanium’s capabilities across industries.
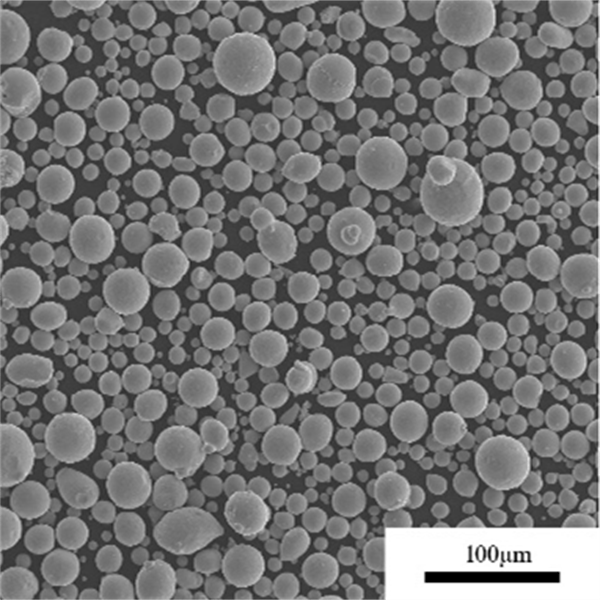
Global Supply and Production of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder production methods, volumes, quality, costs, and sustainability have a major influence on applicability.
Major manufacturing countries:
| Country | Key Players |
|---|---|
| USA | ATI, Carpenter Tech, Puris |
| UK | Praxair, Metalysis |
| Germany | GfE, TLS |
| China | Baoji, Zunyi, Luoyang |
| Japan | Toho, OSAKA |
| Russia | VSMPO |
Production processes:
| Method | Description | ParticleCharacteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma atomization | High purity, spherical powder | Very flowable |
| Gas atomization | Medium purity, spherical | Flowable |
| Rotating electrode process | Low cost, lower purity | Irregular shape |
| Hydride-dehydride | From titanium scrap | Angular, porous |
| Electrolysis | From titanium ores | Dendritic flakes |
Plasma and gas atomization are preferred for critical applications demanding spherical morphology and purity. Rotating electrode provides cost-savings for less demanding uses. Overall, gas atomization strikes the best balance across quality and economics.
Regional titanium sponge and ingot supply chains also impact powder production economics. Abundant reserves of titanium ores favor production in China and Russia while recycling drives much capacity in the USA and Europe.
Pricing:
| Titanium Powder Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| CP Grade 1 | $50-150 per kg |
| CP Grade 2 | $75-200 per kg |
| Ti 6Al-4V Grade 5 alloy | $80-250 per kg |
| High purity spherical | $500-2000 per kg |
Pricing depends strongly on purity, chemistry, particle size distribution, and spherical morphology. Reducing contamination and maintaining powder quality necessitate greater processing and controls – driving costs higher. Larger quantities also benefit from scale economics.
Applications of Titanium Powder
Titanium’s unique balance of strength, corrosion performance, and biocompatibility lend the material and its alloys to varied applications across industries.
Industries using titanium powder:
- Aerospace – aircraft engines and airframes
- Medical – implants, devices, equipment
- Automotive – valves, connecting rods, turbochargers
- Chemical plants – pumps, vessels, heat exchangers
- Marine – propellers, offshore platform components
- Sports – golf clubs, tennis rackets, bicycles
- Additive manufacturing
Titanium powder products:
| Category | Application Examples | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace components | Turbine blades, landing gear, fasteners, structural brackets | High strength, temperature resistance |
| Biomedical implants | Knee, hip joints, dental, spinal fusion devices | Biocompatibility, osseointegration |
| Automotive parts | Connecting rods, valves, springs, turbocharger wheels | High strength, fatigue resistance |
| Chemical equipment | Tanks, piping, reaction vessels, heat exchangers | Corrosion resistance |
| Consumer goods | Watches, eyeglass frames, bicycles, sports gear | Strength, aesthetics |
| Additive manufacturing | Aerospace, automotive prototypes and end-use parts | Design freedom, lightweighting |
By leveraging titanium’s strengths across these areas, engineers can:
- Reduce weight in moving components
- Customize biomedical implants
- Build highly loaded structures
- Withstand harsh operating environments
- Exploit design freedom of AM
And overcome limitations of:
- Heavier, corrodible metals
- Rejection of implants
- Fracture-prone or bulky parts
- Frequent replacement of equipment
- Design constraints of conventional techniques
Metal Additive Manufacturing with Titanium Powder
One of the fastest growing uses of titanium powder is in additive manufacturing, often called 3D printing. Unique capabilities result.
Benefits of additive manufacturing:
- Design freedom – create complex geometries not possible otherwise
- Reduce weight via lattices, thin walls, topology optimization
- Consolidate assemblies to printed parts
- Customized biomedical implants tailored to patient anatomy
- Reduced material waste – only use required powder per part
AM process comparisons:
| Process | Description | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder bed fusion | Laser or e-beam melts powder layers | Medium to high accuracy | Lower build size, slower than DED |
| Directed energy deposition | Focused heat source melts powder stream | Larger components, higher deposition rates | Lower accuracy, higher finishing allowance |
Parameters – powder bed:
| Parameter | Typical range |
|---|---|
| Layer thickness | 20-100 microns |
| Laser power | 100-500 W |
| Scan speed | Up to 10 m/s |
| Beam diameter | 30-100 microns |
AM machine comparisons:
| Machine Brand | Key capabilities |
|---|---|
| EOS M series | High accuracy, ease of use |
| Concept Laser M series | Largest build volumes |
| SLM Solutions | Robust, high productivity |
| Velo3D | Advanced alloys, quality |
| Sciaky | Largest components |
With high beam intensities melting the titanium powder feedstock, near full density parts with tailored microstructures can be fabricated. Heat treatments can further enhance final properties.
The flexibility of AM lets engineers customize parts based on loading needs and optimize designs. With no hard tooling, design changes can rapidly be implemented.
Choosing Titanium Grade and Chemistry
With varied powder grades available, the optimal chemistry depends on application requirements balancing performance, manufacturability, and costs.
Alloy choice considerations:
| Alloy | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP Grade 1-4 | 99.5-99.9% pure Ti | Excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | Lower strength than alloys |
| Ti 6Al-4V ELI | >99.7% Ti, 6% Al, 4% V | Highest strength, hardened via heat treatment | Less biocompatible due to V content |
| Ti 6Al-7Nb | 6% Al, 7% Nb | Aerospace use, Nb stabilizes properties at high temperatures | Less commonly used than Ti 6-4 |
| Ti 5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr | 5% each alloying elements | Highest fatigue strength | Heaviest alloy of group. Contains V. |
Considerations for AM use:
- Higher oxygen, nitrogen limits than wrought alloys
- Lack of cracking during builds
- Optimized for AM processing windows
- Post-build heat treatment capabilities
- Lower powder reuse compared to conventional titanium grades
Quality Control and Specifications
Maintaining strict quality control and meeting aerospace specifications is crucial when producing titanium powder for mission-critical applications.
Quality Control and Specifications
| Parameter | Details | Test Methods |
|---|---|---|
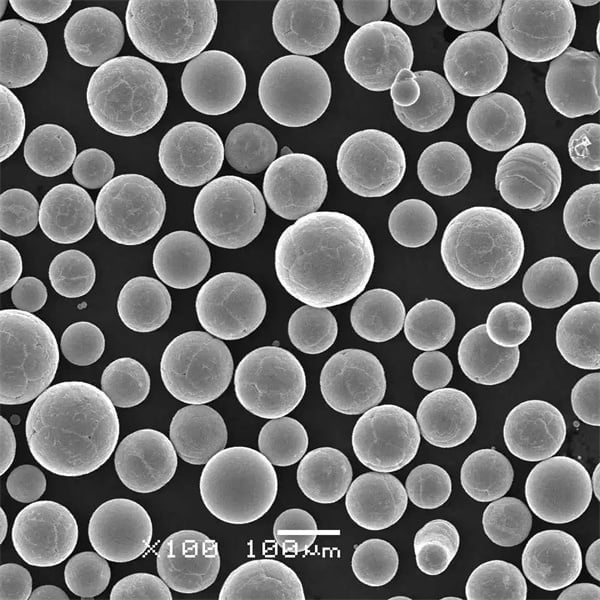
| Particle shape and morphology | Spherical particles promote better powder flow and packing | Imaging using SEM, optical microscopy |
| Chemistry – compositions and impurities | Determines final material properties | ICP, mass spectroscopy, LECO analysis |
| Apparent density and tap density | Key indicators of powder reuse suitability | Hall flowmeter funnel tests |
| Powder reuse | Reusing powder can introduce contamination | Testing of reused powder against fresh |
Meeting certification standards like ISO 9001, AS9100D, or Nadcap ensures powders satisfy aerospace requirements. Common documents include AMS, ASTM, AWS, and custom specifications by major companies.
Global Trade of Titanium Powder
As titanium powder finds increased use globally across industries, trade between countries continues strengthening.
Major exporters:
- USA
- Japan
- UK
- Germany
Major importers:
- China
- USA
- Germany
- France
- Italy
China’s rapidly growing manufacturing sectors pull in titanium powder that domestic producers cannot fully supply. The USA, Europe and Japan export higher grade titanium to serve this demand.
Increasing adoption of additive manufacturing is also forcing companies to import titanium powder to prototyping or produce complex components. Lead times for custom alloys can span months.
Trade data details:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Annual demand growth | 8-12% CAGR forecast |
| Ports handling Ti powder | Hamburg, Shanghai, Tokyo, LA/Long Beach |
| Duties | Typically 0-5% for titanium minerals, powders, scrap |
| Documentation | Proforma invoices, certificate of origin, SDS sheets |
| Private market pricing | 20-50% premiums for rapid delivery |
With titanium making deeper inroads and supply lagging demand in many regions, global trade fills this gap despite logistics and shipping challenges. Many forward-looking agreements secure multi-year powder supplies.
Storage and Handling Best Practices
While titanium powder offers many benefits, the fine particle size mandates careful handling to prevent contamination, dust explosions, or leaks into the environment.
Key properties affecting handling:
- Reactive fine metallic powder
- Flammability risk with varied particle size fractions
- Tendency to cold weld under compression
- Hydrogen absorption and embrittlement
Handling guidelines:
- Inert gas glove boxes for high purity powders
- Grounding to avoid static discharge
- Cleanrooms to control contamination
- Moisture-proof packaging with desiccants
- Dry nitrogen purging of transport containers
- Limited reuse to minimize impurity uptake
Carefully designed facilities and standard operating procedures enable titanium powder producers and users to leverage the materials strengths while safely managing risks. Proper protective equipment for workers is also essential.
Regulatory controls on powder plants and transportation channels continue tightening as well across different countries.
Future Outlook
With expanding applications across aerospace, biomedical, automotive, and additive manufacturing, demand for titanium powder continues growing over 8% yearly. New production methods, higher volumes, and better recycling will improve availability.
Key trends influencing sector growth:
- Lightweighting in mobility – airframes, engines, vehicles
- Customized medical implants using AM
- Corrosion resistance needs in chemical environments
- Higher strength requirements and extreme operating conditions
- Compact equipment sizes favor high performance materials
Overcoming limitations around lead times, supply security, costs, and quality will be crucial for titanium powder producers targeting rapid growth across these areas.
FAQs
Q: What makes titanium powder suitable for aerospace and aircraft use?
A: Titanium offers the best strength-to-weight ratio among metals, making it ideal for reducing weight in flight critical rotating parts as well as structural brackets and components. It can also withstand extreme temperatures and stresses for engine applications.
Q: Why is titanium popular for biomedical implants and devices?
A: Titanium strongly bonds to bone through a process called osseointegration without immune rejection. This makes it suitable for orthopedic joint replacements. It also exhibits biocompatibility within the human body environment making it useful for surgical tools and medical equipment.
Q: How does titanium powder differ from titanium bar or plate forms?
A: Titanium powder provides feedstock for near net shape part fabrication and additive manufacturing. This allows maximizing buy-to-fly ratios compared to machining large amounts of material. The high surface area also promotes chemical interactions and heat transfer useful in some catalysts and heat exchangers.
Q: What is the typical price range for common titanium powder grades and is pricing expected to decline?
A: Commercially pure grade 1 titanium powder costs around $50-150 per kg while workhorse Ti 6Al-4V alloy powder is $80-250 per kg. Prices depend heavily on quality, production method, order volume and geographical factors. Supply shortages likely mean titanium powder stays at a premium versus base metals or steel powder. Recycling and new processes can help manage costs.
Q: What are the major challenges around shipping and transporting titanium powder internationally?
A: Titanium powder’s high affinity for air or moisture can lead to fires if not properly handled. Fine particle sizes also pose dust explosion risks. Special moisture-proof containers, nitrogen purging, regulated labeling, grounding, and safety documentation help provide safe international transport of titanium feedstocks to manufacturers across borders.