gas atomizer equipment produces fine spherical metal powders with controlled particle size distribution critical across metal AM, thermal spray, MIM and other powder metallurgy applications. This guide covers process principles, atomizer types, system components, operating parameters, manufacturers and comparative assessment.
gas atomizer equipment Process Overview
Gas atomization uses kinetic energy from high velocity gas jets to disintegrate molten metal streams into fine droplets rapidly solidifying into powder:
| Principle | Breakup of metal stream into fine droplets by gas impingement |
| Gas types | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Metal types | Nickel, Iron, Cobalt alloys |
| Scales | Lab, Pilot, Industrial |
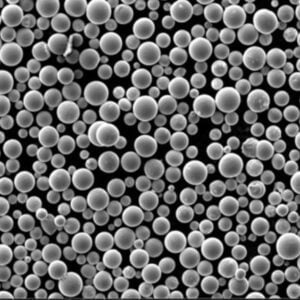
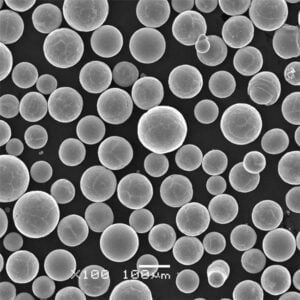
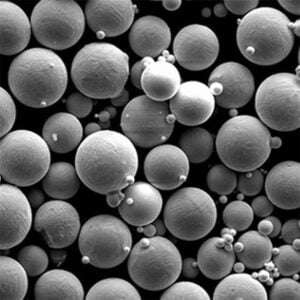
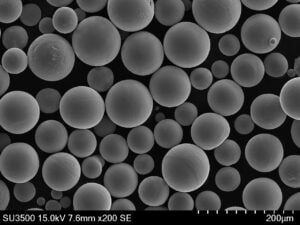
| Powder attributes | Controlled PSD, High sphericity, Surface chemistry uniformity |
| Particle sizes | 3 microns to 120 microns |
| Products | Alloy powders, Master alloys |
| Industries | Metal AM, MIM, Coatings |
Gas atomized powders offer precise property control but require higher capital investment than other atomization techniques.

gas atomizer equipment Types
| Atomizer | Details |
|---|---|
| Close-coupled | Nozzle and gas integration allows very fine 20 micron powders |
| Free-fall | Molten metal stream falls through gas chamber for support-free operation |
| Rotary | Reliable performance for high alloy steels via rotating metal pour tubes |
Emerging Designs
Multi-nozzle cluster atomization and centrifugal atomizers up productivity. Ultrasonic atomization and electrode induction gas atomizers simplify free-fall powder production.
System Components
Key modules in complete industrial gas atomization systems include:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Melting furnace | Induction melting of metals to superheat state |
| Nozzle assembly | Controls molten metal stream injection into gas chamber |
| Gas control | Regulates gas type, pressure and flow dynamics |
| Droplet solidification | Rapid cooling transforms droplets into powders |
| Collection system | Sieving separates powder by particle size |
| Baghouse | Captures ultrafine solidified particles from gas exhaust |
| Recycling | Reintroduces unused gas and oversize particles |
Precise monitoring and tightly integrated feedback control between above modules is critical for powder quality consistency.
Process Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Range | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Metal temperature | 30-100°C superheat | Fluidity, surface oxidation |
| Nozzle orifice size | 2mm-6mm | Droplet size, flow dynamics |
| Gas type | N2, Ar | Cooling rate, surface chemistry |
| Gas pressure | 5-15 barg | Particle size distribution |
| Gas flow rate | 0.1-3 m3/min | Atomization efficiency and yield |
| Drop height | 2-10m | Solidification time and powder characteristics |
The interdependent relationships between these parameters necessitate empirical optimization guided by computational models to achieve powder requirements.
gas atomizer equipment Suppliers
| Company | Capacity Range | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| AP&C | 10kg/hour – 300kg/hour | $750,000-$4 million |
| PSI | 25kg/hour – 500kg/hour | $950,000-$6 million |
| Gasbarre | 50kg/hour – 1000kg/hour | $1.2 million – $8 million |
| Buhler Group | 500kg/hour – 35,000kg/hour | $6 million+ |
Larger production scales carry exponentially higher price tags. Significant custom engineering required.
Comparative Assessment
| Close-coupled Atomizer | Free-fall Atomizer | |
|---|---|---|
| Investment cost | High | Medium |
| Complexity | High – Integrated nozzle-gas design | Medium – Decoupled components |
| Maintenance | Challenging – Entire vessel handling | Easier – Modular parts |
| Productivity for fine powders | Higher | Medium |
| Material flexibility | Medium – Limited by nozzle clogging risks | High – open architecture |
| Process monitoring | Tight process control enabled | Relies more on characterization |
Key Takeaways
- Precision particle engineering with wide flexibility makes gas atomization a powerful but costly technique
- Integrated modeling and monitoring enables quality powders with narrow specifications
- Scalability remains a key limitation across small, medium and large gas atomizers

FAQs
Q: What size gas atomization systems are best suited for metal AM powder needs?
A: Benchtop lab atomizers from 1-5kg/hour scale are appropriate for R&D. For commercial metal AM production, 50-200kg/hour atomizers balance throughput, cost and powder quality needs.
Q: What gas pressure is typically used in atomization?
A: Most gas atomization relies on pressures from 5-12 barg. Higher pressures facilitate finer powders but require heavier duty vessels. Argon allows faster heat extraction than nitrogen.
Q: How small can gas atomizer particle size reach?
A: Leading edge close-coupled nozzle atomizers have demonstrated consistent production of metal powders approaching 15-20 microns while still maintaining reasonable yield percentages.
Q: What metals are not suitable for gas atomization?
A: Highly reactive alloys like titanium and aluminum alloys pose oxidation challenges and risk nozzle clogging. Induction skull melting helps alleviate these issues.